| When applying a linearly polarized beam with the polarization plane aligned at 45deg to the waveplates principal plane, the output beam will be circularly polarized. Similarly when applying a circularly polarized beam to a ¦Ë/4 waveplate the output beam will be linearly polarized. When a quarter waveplate is double passed, i.e. by mirror reflection, it acts as a half waveplate and rotates the plane of polarization to a certain angle. Quarter waveplates are widely used in creating circular polarization from linear or linear polarization from circular, ellipsometry, optical pumping, suppressing unwanted reflection, optical isolation and etc. |
 |
|
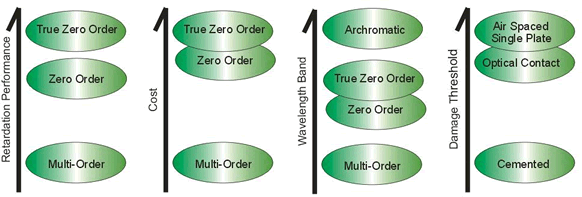
Firstly, you should know the retardation, is it a half waveplate or a quarter waveplate? Or even a special retardation? Then, you should know the size and working wavelength. This is important for waveplate. The retardation is different at different wavelength. It depends on wavelength. After confirm these conditions, we should choose a type of waveplate. If temperature bandwidth and wavelength bandwidth is important for you, you should choose zero order or true zero order. For zero order, optical contacted has better wavefront distortion and parallelism, air spaced has high damage threshold. True zero order is better than zero order waveplate at all parameters and can be used at more critical application. When temperature bandwidth and wavelength bandwidth is not a problem for you, multi order is a better choice, it is cheap. If a zero order or true zero order waveplate does not offer retardance over a wide enough wavelength band, one solution is to use an achromatic waveplate, it has over hundreds of nanometers bandwidth. For detailed information, please refer to above table or contact us.
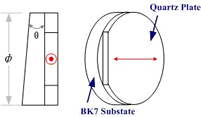 Sometimes, the waveplate has unwanted Etalon effect, in order to eliminate this effect, Union Optic offer Wedge Waveplate to solve this problem. For detailed information, please contact us. Sometimes, the waveplate has unwanted Etalon effect, in order to eliminate this effect, Union Optic offer Wedge Waveplate to solve this problem. For detailed information, please contact us.
Due to the rotation activity of natural quartz crystal, it also can be used as polarization rotators so that the plane of input linearly polarized beam will be rotated at special angle which is determined by the thickness of quartz crystal. Left-handed and right-handed rotators can be offered by Union Optic now. |